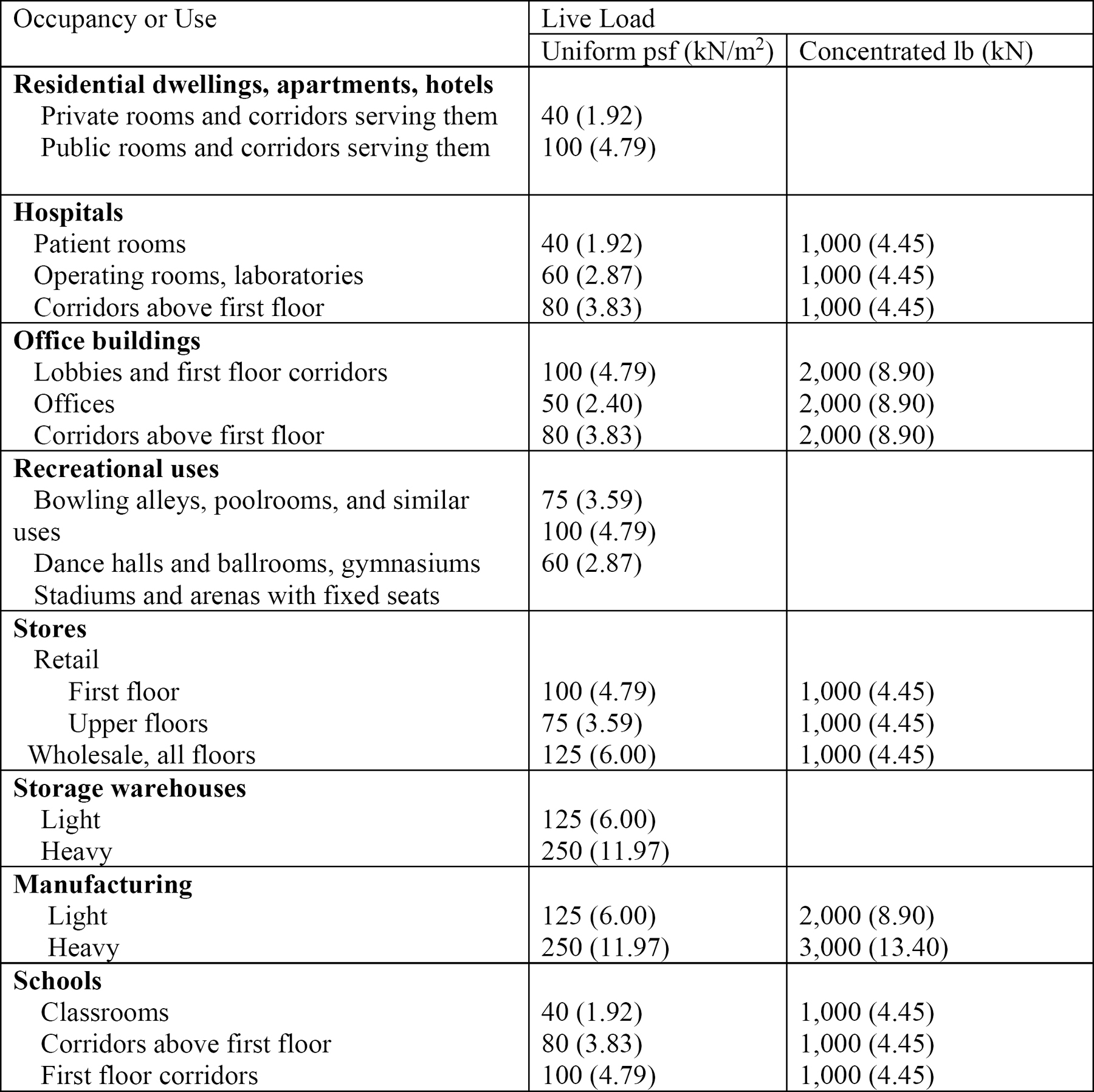
For an office building the live load is normally a uniform load of 50 pounds per square foot psf over the entire floor area for a framing member or a 2 000 pound load placed upon any 2 1 2 x 2 1 2 square foot space.
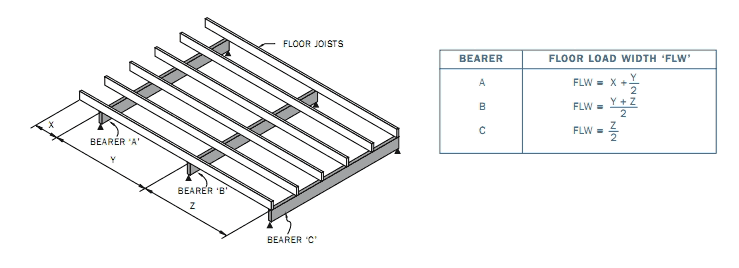
Floor load width explained.
Critical reinforcement beam stress and deflection conditions occur based upon maximum wheels loads for the floor beams joists spaced less than 8 0.
A room used solely for sleeping might need to carry only 30 psf whereas a garage floor over a basement would need 50 psf or higher.
Floor load width flw 78.
A typical wood frame floor covered with carpet or vinyl flooring has a dead load of about 8 pounds per square foot.
If there s wall board covered ceiling suspended from the underside of that floor the dead load increases to about 10 pounds per square foot.
The load producing the greatest stress in a framing member is the governing load for that member.
The dead load on a floor is determined by the materials used in the floor s construction.
Floor loads whether the bearers are supporting load bearing walls or only floor loads the area of the floor supported by an individual bearer must be determined.
Where the bearer supports load bearing walls the type of roof covering also needs to be determined.
In order to reduce size and or height of the reinforcing beam under the tracks reduce the track spacing as required.
First floor live loads have higher requirements than second floor live loads 40 pounds per square foot vs.
Example flw floor if x 2000mm load width y 4000mm a 900mm flw a x 2 a flw a 1900mm flw b x y 2 flw b 3000mm flw c y 2 flw c 2000mm 79.
This is referred to as the floor load width flw.
The load is an average value.
A floor joist appropriately selected to span 10 feet with an l 360 limit will deflect no more than 120 360 1 3 inches under maximum design loads.
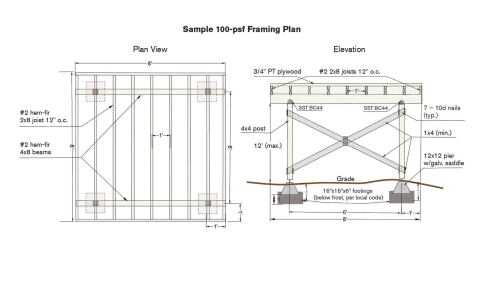
Bearer floor joist design example simple rectangular shaped light weight home floor joists bearers 3600 section gable roof 25o pitch steel sheet.