At the instant of heel contact there is zero force between the foot and the floor due to the fact that the heel strike is defined the moment when contact is generated but there is no force production at that time instant.
Floor reaction force heel strike.
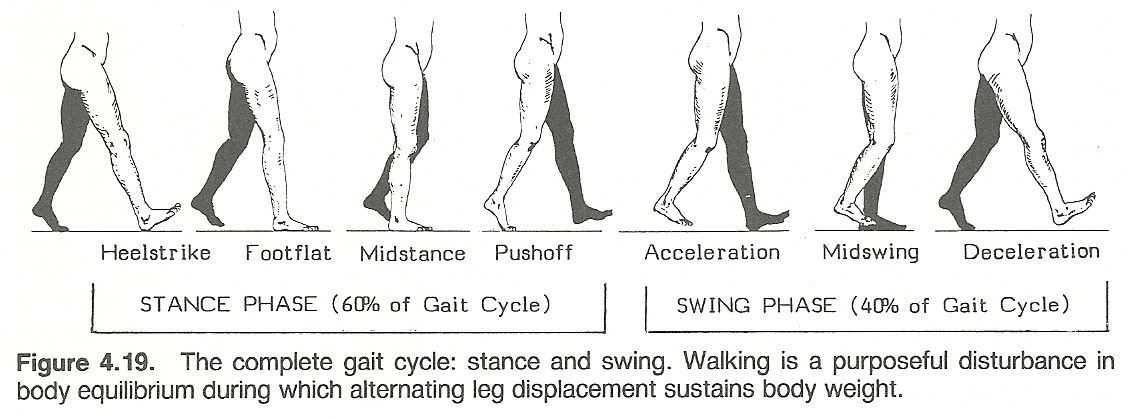
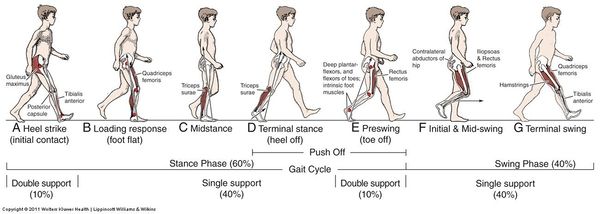
For example if heel strike is the initial contact the gait cycle for the right leg is from one heel strike to the next heel strike on the same foot.
Ankle dorsiflexion weakness results in a lack of heel strike and decreased floor clearance.
This force sends a shock wave up through the body via the skeletal system.
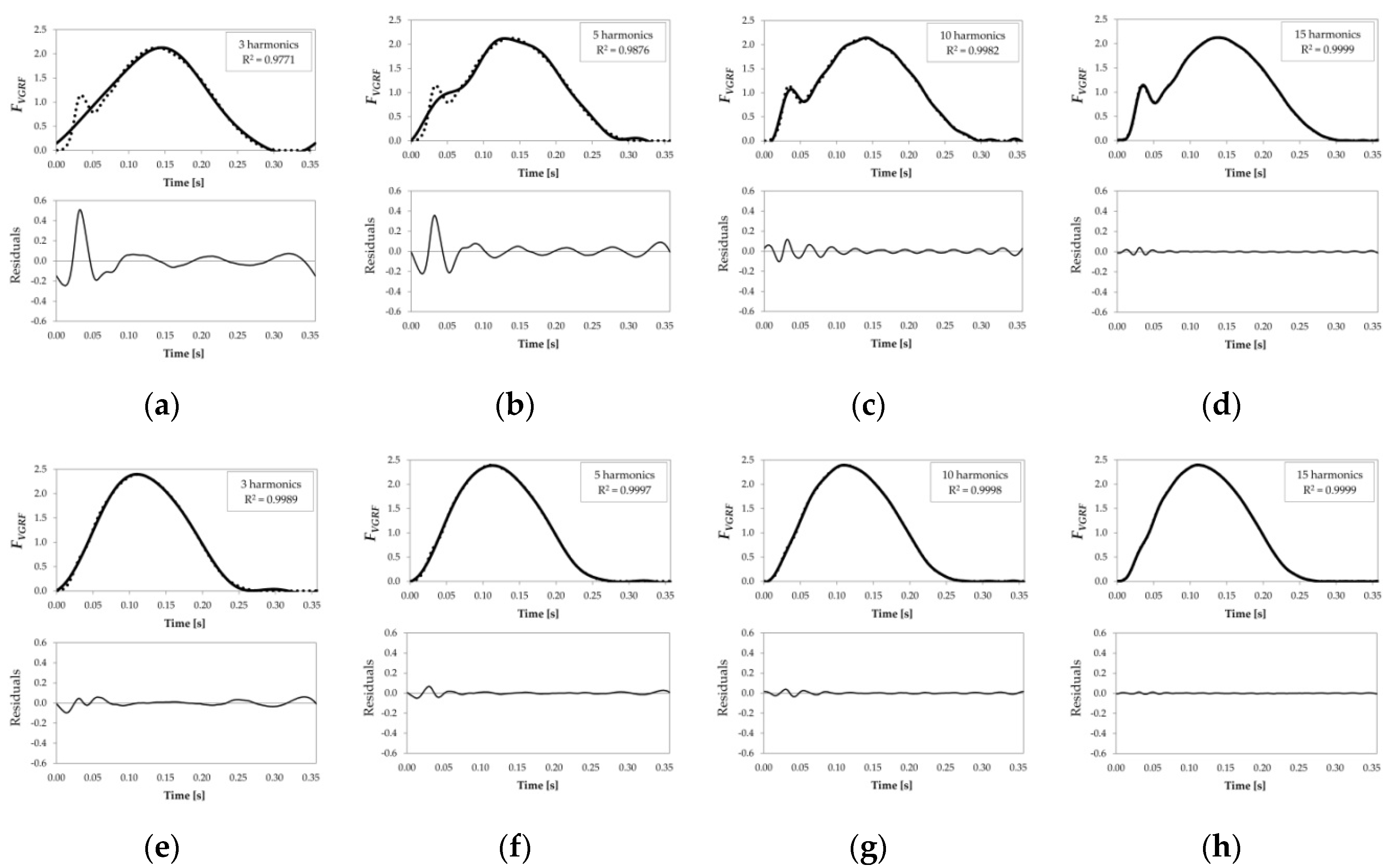
In heel striking the collision of the heel with the ground generates a significant impact transient a nearly instantaneous large force.
Figure 1 21a shows the contact area when standing barefoot on both feet.
Loading rate has decreased.
It is synonymous with the stride length.
The definition offered by perry 11defines heel strike initial contact as the moment when the foot just touches the floor.
In forefoot striking the collision of the forefoot with the ground generates a very minimal impact force with no impact transient.
The contact area is much smaller than the area of the base of support.
By eliminating the heel strike the runner has eliminated the impact peak and the initial slope of the rising force is now lower.
Several studies report that the vertical force passing through the foot reaches its highest peak just before lift off.
Control of one or more of these floor reaction forces is a viable means of controlling the alignment and or phasic motions of the foot ankle complex throughout the stance phase thereby preventing injury.
All the elements of the muscle mesh intersected by the cross section plane contributed to the longitudinal force.
This is the ground reaction force generated when heel strike running in shoes.
The ground reaction force is distributed across the whole of the area of contact between the feet and the floor.
While this definition is appropriate for normal gait it does not describe the typical heel strike in many impaired populations.
Calf tightening or contractures due to a period of immobilisation or trauma will cause reduced heel strike due to restricted dorsiflexion.
At the end of the heel strike and the loading response steps the longitudinal force inside each thigh s muscle was computed.